
Lung cancer is an adenocarcinoma that develops in the airway of parenchyma of the lung. Whereas mesothelioma develops in the pleura of the lungs. The risk of developing lung cancer increases greatly in smokers who have been exposed to asbestos. Smoking weakens the lungs, contributing to the negative health effects of asbestos exposure.
Smoking and asbestos exposure can cause lung cancer. If you are a smoker who breathes air containing asbestos fibers, your risk of getting lung cancer can be 100 times greater.
Advanced lung cancer has similar symptoms to those of mesothelioma including:
Coughing up blood is also a common symptom of advanced lung cancer.
Lung cancer is initially detected through periodic CT scans. Low dose CT scans are now being used for early detection of lung cancer. The earlier lung cancer is detected the better the prognosis and outcome.
Following a CT scan or another radiological scan, a biopsy of the growth on the lung is taken and examined by an expert pathologist for diagnosis. The biopsy is usually performed with a bronchoscope or a needle centesis.
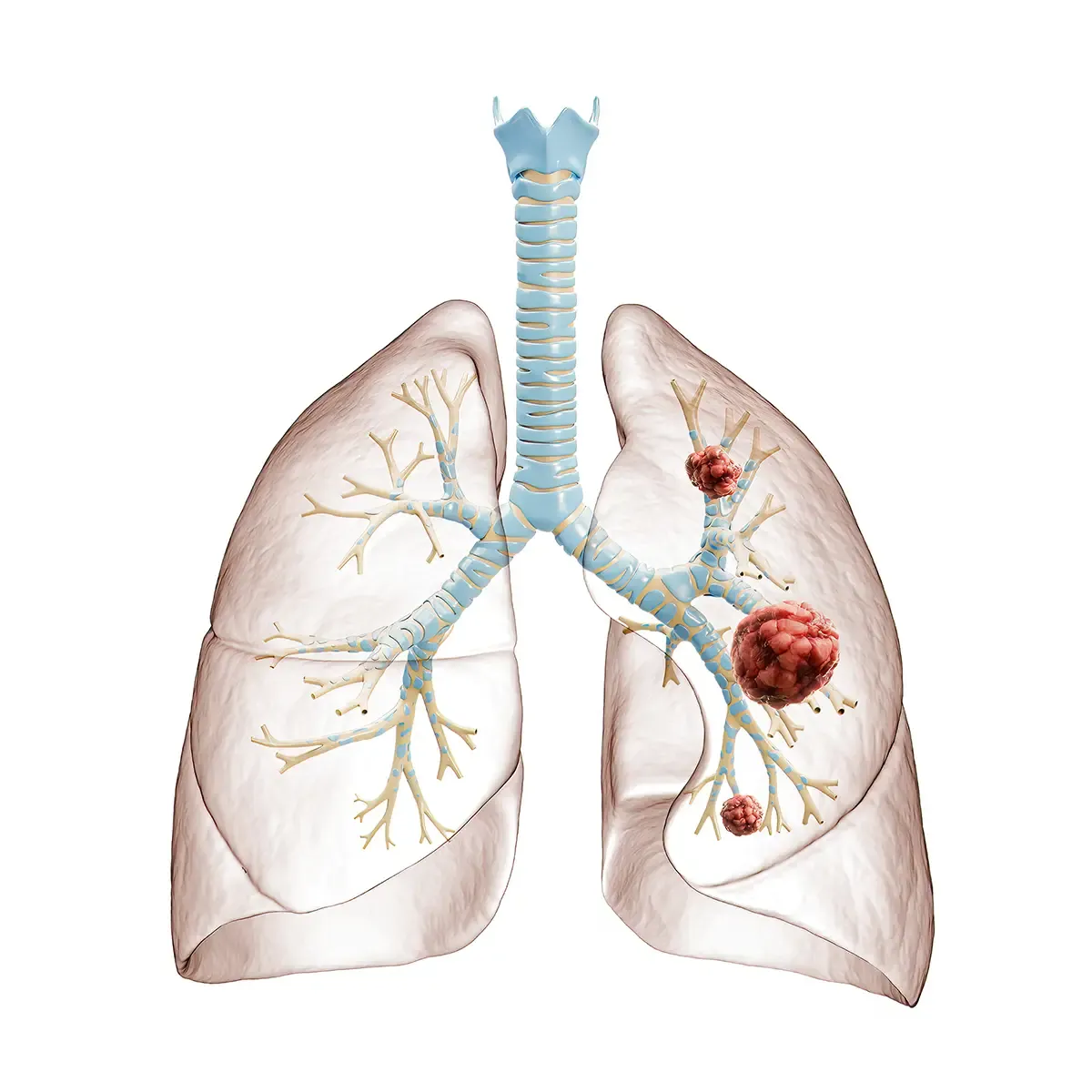
Lung cancer, unlike mesothelioma and asbestosis, can be cured. The use of low dose CT scans for early detection has led to better outcomes in more recent years. When detected early, lung cancer can be surgically removed. Follow up chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy are then used to further improve prognosis, or possibly for palliative therapy.


Website designed by c4 Digital Agency